Economic growth is an increase in real GDP; it means an increase in the value of goods and services produced in an economy.
The rate of economic growth is the annual percentage increase in real GDP. There are several factors affecting economic growth, but it is helpful to split them up into:
- Demand-side factors (e.g. consumer spending)
- Supply-side factors (e.g. productive capacity)
Economic growth in the UK
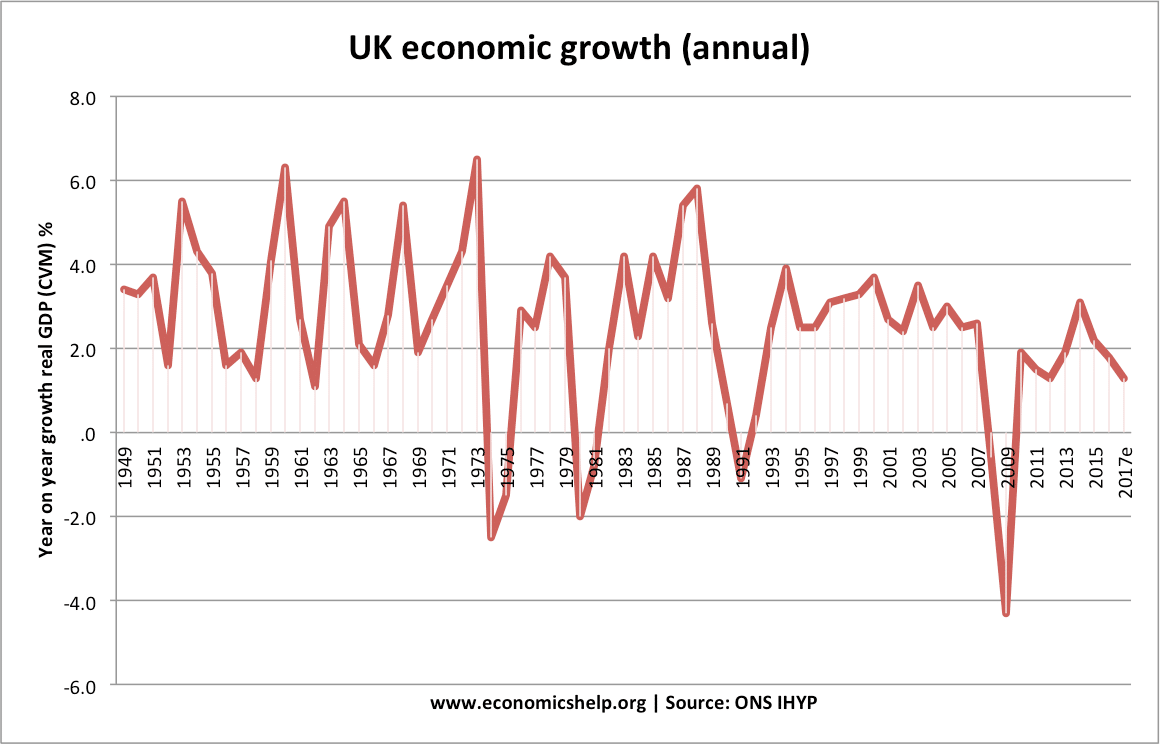
Annual UK economic growth 1949-2017
Demand side factors – Aggregate Demand (AD)
AD= C+I+G+X-M.
Therefore a rise in Consumption, Investment, Government spending or exports can lead to higher AD and higher economic growth.
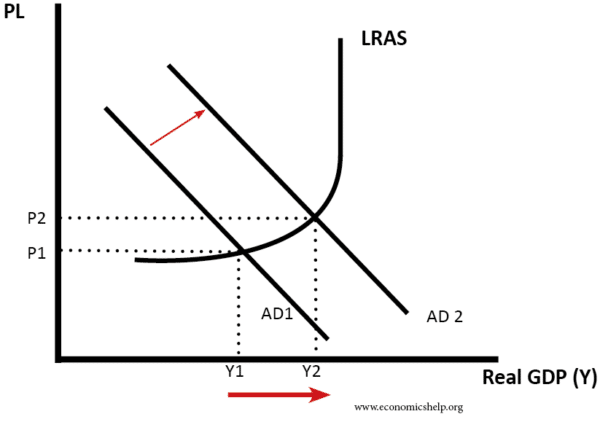
Graph showing rise in AD
What could affect AD?
- Interest rates. Lower interest rates would make borrowing cheaper and should encourage firms to invest and consumers to spend. People with mortgages will have lower monthly mortgage payments so more disposable income to spend. However, 2009-16 we had a period of very low-interest rates, but due to low confidence and reluctant bank lending, economic growth was still sluggish.
- Consumer confidence. Consumer and business confidence is very important for determining economic growth. If consumers are confident about the future they will be encouraged to borrow and spend. If they are pessimistic they will save and reduce spending.
- Asset prices. Rising house prices create a positive wealth effect. People can re-mortgage against the rising value of their home and this encourages more consumer spending. House prices are an important factor in the UK because so many people are homeowners.
- Real wages. Recently, the UK has experienced a situation of falling real wages. Inflation has been higher than nominal wages, causing a decline in real incomes. In this situation, consumers will have to cut back on spending – in particular reducing their purchase of luxury items.
- Value of exchange rate. If the Pound devalued, exports would become more competitive and imports more expensive. This would help to increase demand for domestic goods and services. A depreciation could cause inflation, but in the short term at least it can provide a boost to growth.
- Banking sector. The 2008 Credit crunch showed how influential the banking sector can be in determining investment and growth. If the banks lose money and no longer want to lend, it can make it very difficult for firms and consumers leading to a decline in investment.
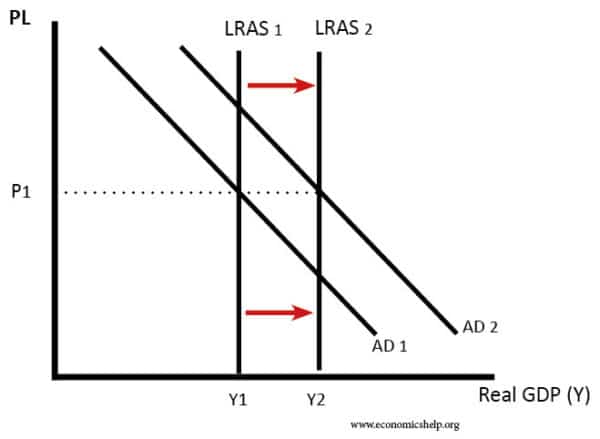
Factors that determine long run economic growth
In the long run, economic growth is determined by factors which influence the growth of Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS). If there is no increase in LRAS, then a rise in AD will just be inflationary.
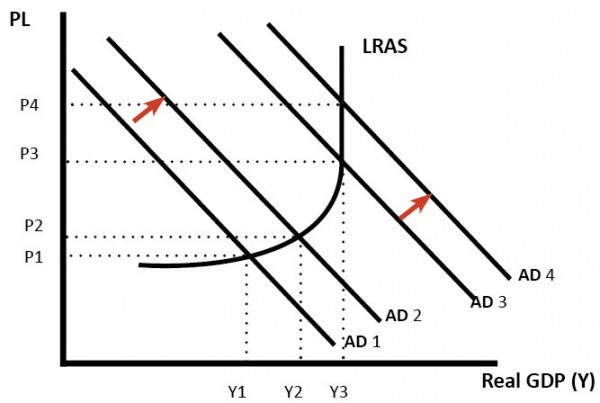
Classical view
This graph shows an increase in LRAS and AD, leading to an increase in economic growth without inflation.
LRAS (productive capacity) can be influenced by
- Levels of infrastructure. Investment in roads, transport and communication can help firms reduce costs and expand production. Without the necessary infrastructure, it can be difficult for firms to be competitive in the international markets. This lack of infrastructure is often a factor holding back some developing economies.
- Human capital. Human capital is the productivity of workers. This will be determined by levels of education, training and motivation. Increased labour productivity can help firms take on more sophisticated production processes and become more efficient.
- Development of technology. In the long run development of new technology is a key factor in enabling improved productivity and higher economic growth.
- The strength of labour markets. If labour markets are flexible, then firms will find it easier to hire the workers they need. This will make expansion easier. Highly regulated markets could discourage firms from hiring in the first place.
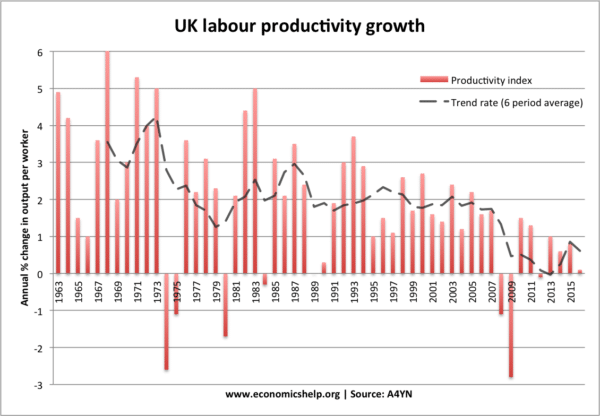
The role of productivity
Productivity is output per worker and has a strong bearing on the long-run trend rate of economics growth. Productivity will be determined by technology, levels of investment in new technology and the skills of the labour force.
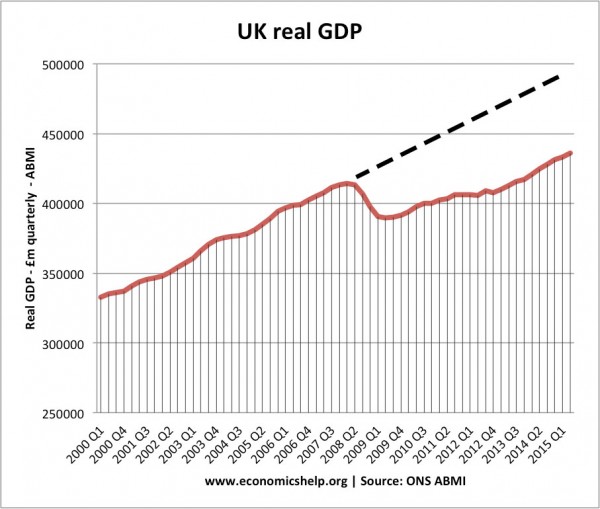
This shows a fall in productivity growth since the 2007 recession – leading to lower rates of economic growth.
Other factors that can affect growth in the short term
- Commodity prices. A rise in commodity prices such as a rise in oil prices can cause a shock to growth. It causes SRAS to shift to the left leading to higher inflation and lower growth.
- Political instability. Political instability can provide a negative shock to growth.
- Weather. The exceptionally cold December in UK 2010, led to a surprise fall in GDP
- Annual Rate of Economic Growth in the UK
Examples of Economic Growth
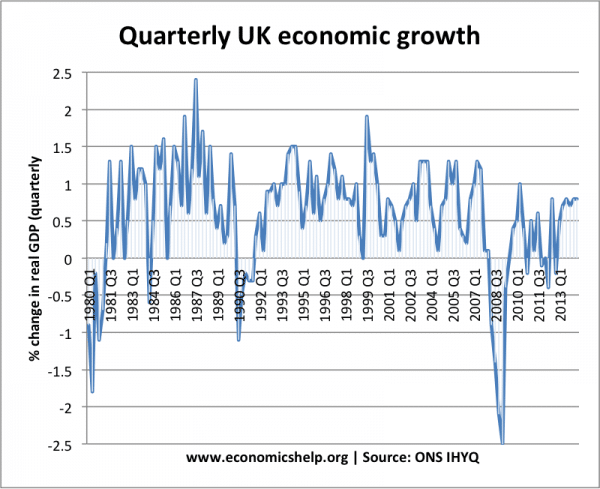
A graph showing quarterly economic growth in UK. In 1981,1991 and 2008 we see a recession.
In 1981, this negative economic growth was due to:
- Higher interest rates (reducing borrowing)
- Lower government spending (tight fiscal policy)
- Appreciation in the value of the pound which made exports uncompetitive.
In the mid-1980s, the high economic growth was caused by
- Rising consumer confidence
- Relatively low real interest rates
- Rising wages
- Rising house prices causing a rise in wealth and consumer spending
- Supply-side reforms such as privatisation and tax cuts.
In 2009, the sharp fall in Real GDP (negative economic growth) was caused by:
- Higher oil prices reducing living standards
- Global credit crunch leading to a fall in bank lending and investment
- Fall in house prices causing lower wealth and spending
The great moderation 1992-2007
This was a long period of economic expansion in the UK.
- It was helped by technological developments – rapid improvements in computers/internet/mobile phones improving productivity growth
- Stable inflationary environment. Bank of England given control of monetary policy in 1997.
- Great moderation 1992-2007