Definition of fiscal policy. Fiscal policy involves the government changing the levels of taxation and government spending in order to influence Aggregate Demand (AD) and the level of economic activity.
- AD is the total level of planned expenditure in an economy (AD = C+ I + G + X – M)
The purpose of Fiscal Policy
- Stimulate economic growth in a period of a recession.
- Keep inflation low (UK government has a target of 2%)
- Fiscal policy aims to stabilise economic growth, avoiding a boom and bust economic cycle.
Fiscal policy is often used in conjunction with monetary policy. In fact, governments often prefer monetary policy for stabilising the economy.
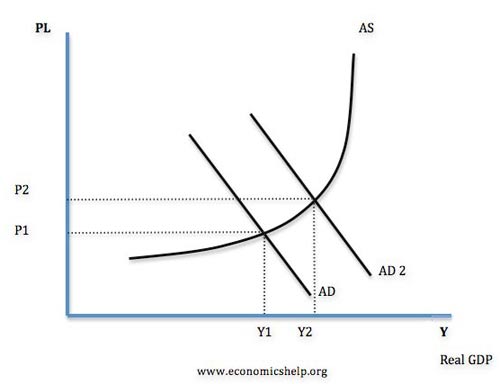
Expansionary (or loose) Fiscal Policy
- This involves increasing AD.
- Therefore the government will increase spending (G) and cut taxes (T). Lower taxes will increase consumers spending because they have more disposable income (C)
- This will tend to worsen the government budget deficit, and the government will need to increase borrowing.
Diagram showing effect of expansionary fiscal policy
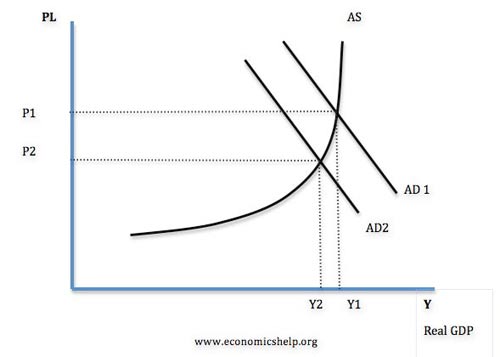
Deflationary (or tight) Fiscal Policy
- This involves decreasing AD.
- Therefore the government will cut government spending (G) and/or increase taxes. Higher taxes will reduce consumer spending (C)
- Tight fiscal policy will tend to cause an improvement in the government budget deficit.
Diagram showing the effect of tight fiscal policy
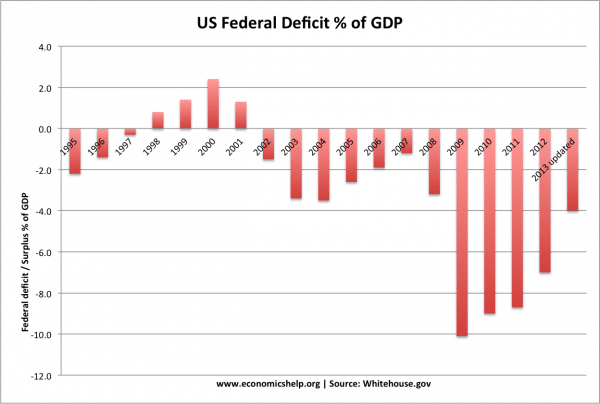
UK fiscal policy
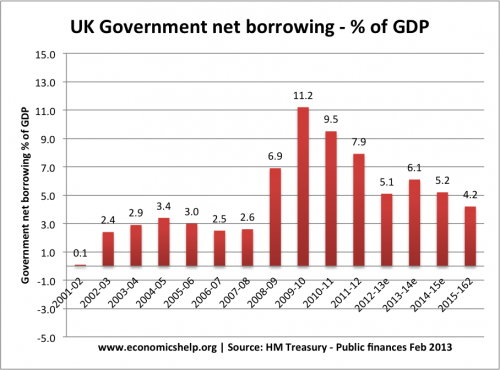
In 2009, the government pursued expansionary fiscal policy. In response to a deep recession (GDP fell 6%) the government cut VAT in a bid to boost consumer spending. This caused a big rise in government borrowing (2009-10). (Government borrowing also rose because of the recession leading to lower tax revenue)
When the new coalition government came into power in May 2010, they argued the deficit was too high and then announced plans to reduce government borrowing. This involved spending limits. These austerity measures were a factor in causing lower economic growth in 2011 and 2012.
Terms relating to fiscal policy
- Fiscal Stance: This refers to whether the government is increasing AD or decreasing AD, e.g. expansionary or tight fiscal policy
- Fine Tuning: This involves maintaining a steady rate of economic growth through using fiscal policy. However, this has proved quite difficult to achieve precisely.
- Automatic fiscal stabilisers – If the economy is growing, people will automatically pay more taxes ( VAT and Income tax) and the Government will spend less on unemployment benefits. The increased T and lower G will act as a check on AD. But, in a recession, the opposite will occur with tax revenue falling but increased government spending on benefits, this will help increase AD
- Discretionary fiscal stabilisers – This is a deliberate attempt by the government to affect AD and stabilise the economy, e.g. in a boom the government will increase taxes to reduce inflation.
- The multiplier effect. When an increase in injections causes a bigger final increase in Real GDP.
- Injections (J) – This is an increase of expenditure in the circular flow, it includes govt spending(G), Exports (X) and Investment (I)
- Withdrawals (W) – This is leakages from the circular flow This is household income that is not spent on the circular flow. It includes: Net savings (S) + Net Taxes (T) + Net Imports (M)
Criticism of fiscal policy
- The government may have poor information about the state of the economy and struggle to have the best information about what the economy needs.
- Time lags. To increase government spending will take time. It could take several months for a government decision to filter through into the economy and actually affect AD. By then it may be too late.
- Crowding out. Some economists argue that expansionary fiscal policy (higher government spending) will not increase AD because the higher government spending will crowd out the private sector. This is because the government have to borrow from the private sector who will then have lower funds for private investment.
- Government spending is inefficient. Free market economists argue that higher government spending will tend to be wasted on inefficient spending projects. Also, it can then be difficult to reduce spending in the future because interest groups put political pressure on maintaining stimulus spending as permanent.
- Higher borrowing costs. Under certain conditions, expansionary fiscal policy can lead to higher bond yields, increasing the cost of debt repayments.
- Criticisms of Fiscal Policy – More detail on criticisms of fiscal policy
Evaluation of fiscal policy
The success of fiscal policy will depend on several factors, such as
- It depends on the size of the multiplier. If the multiplier effect is large, then changes in government spending will have a bigger effect on overall demand.
- It depends on the state of the economy. Fiscal policy is most effective in a deep recession where monetary policy is insufficient to boost demand. In a deep recession (liquidity trap). Higher government spending will not cause crowding out because the private sector saving has increased substantially. See: Liquidity trap and fiscal policy – why fiscal policy is more important during a liquidity trap.
- It depends on other factors in the economy. For example, if the government pursue expansionary fiscal policy, but interest rates rise, and the global economy is in a recession, it may be insufficient to boost demand.
- Bond yields. If there is concern over the state of government finances, the government may not be able to borrow to finance fiscal policy. Countries in the Eurozone experienced this problem in the 2008-13 recession.
Brief history of fiscal policy
- Keynes advocated the use of fiscal policy as a way to stimulate economies during the great depression.
- Fiscal Policy was particularly used in the 50s and 60s to stabilise economic cycles. These policies were broadly referred to as ‘Keynesian’
- In the 1970s and 80s governments tended to prefer monetary policy for influencing the economy. Fiscal policy became more prominent during the great depression of 2008-13